Business corporations are complex entities that play an essential duty in the global economy, promoting not just the exchange of solutions and products but additionally offering chances for investment and employment. Structurally, a service firm is a lawful entity that is separate and distinctive from its owners, offering a critical layer of protection known as restricted liability. This indicates that the personal assets of investors are protected from the corporation's responsibilities. Companies can increase funding by providing supplies, which stand for shares of ownership and can be traded on public markets, offering an unique benefit in regards to development and monetary versatility. register foreign company in california of these entities is generally handled by a board of supervisors chosen by the shareholders, who established wide plans and make decisions important to the well-being of the company.
The functional elements of a company are managed by its officers, consisting of the Chief Exec Policeman (CEO), Chief Financial Policeman (CFO), and others, that supervise daily activities and carry out the strategies established by the board. This framework aids in dispersing obligations and enables specialized administration. Corporations are subject to extensive regulatory settings that determine openness and accountability, primarily to secure investors and the public. They have to frequently reveal economic details, which is essential for investors making educated choices. Additionally, while corporations are praised for their ability to amass funding, they are often looked at for their social and environmental impacts. This has actually caused the surge of company social responsibility (CSR) initiatives targeted at making sure that companies run in such a way that is not just financially successful yet additionally socially and ecologically lasting.
The Function and Structure of Business Firms
Business corporations are pivotal entities in the worldwide economic climate, serving as the engines that drive innovation, employment, and financial growth. Structurally, a company is an intricate entity characterized by its legal difference from its owners, who are shareholders. This splitting up offers shareholders with minimal responsibility, implying their personal possessions are shielded from the corporation's liabilities. The governance of a corporation is normally supervised by a board of directors, chosen by the investors, that makes tactical choices and manages the organization's overall direction. Everyday operations, nonetheless, are managed by execs and policemans designated by the board. This hierarchical framework permits a reliable department of labor yet also demands careful oversight to avoid disputes of rate of interest and guarantee liability. Firms can elevate capital a lot more easily than various other business kinds. They have the capability to provide exclusive and public equity, as well as various sorts of financial debt instruments, that makes them distinctly capable of funding large-scale ventures and expanding their operations internationally. This ability to elevate significant resources, combined with their sturdiness-- since they proceed to exist past the lives of their founders-- makes firms a highly liked model for several entrepreneurs and investors looking for to mitigate individual dangers while going after significant economic tasks.
Secret Parts of Organization Company Structures
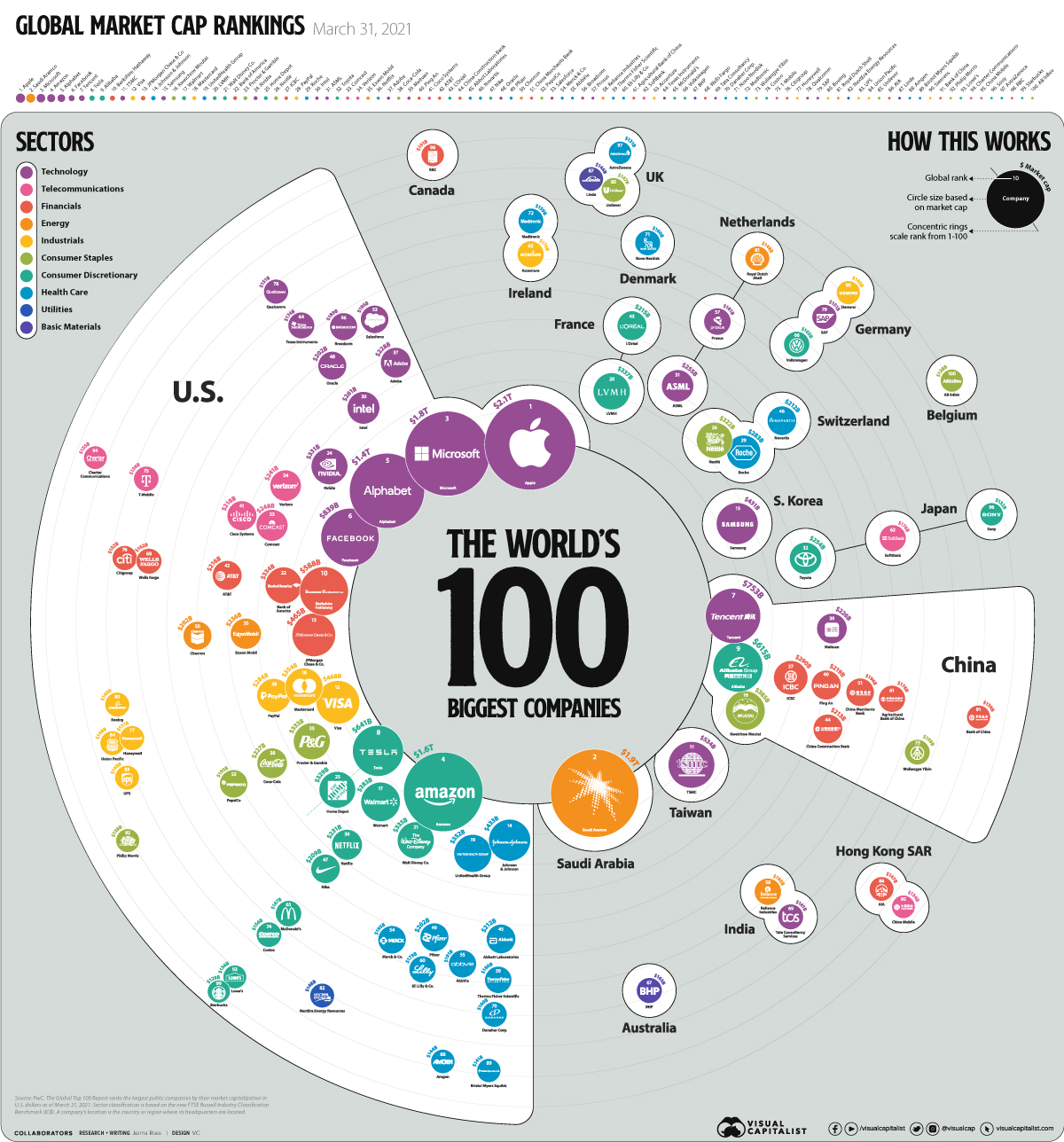
Recognizing the intricacies of business corporation frameworks is important for entrepreneurs, financiers, and legal consultants who navigate the intricate globe of corporate governance and money. At the core of these structures are the board of directors, shareholders, and corporate policemans, each playing an essential role in the operations and tactical direction of the business. The board of supervisors is mainly in charge of managing the company's administration and making certain that shareholder passions are represented and secured. Typically included mouse click the up coming document chosen by the shareholders, the board makes important decisions on business plans and methods, and also picks and oversees the company's executive police officers. Investors, who possess sections of the company with shares of stock, can vote on concerns, including the election of directors and considerable business activities like mergings or purchases. This voting procedure gives investors a means of influencing the firm's direction, though their daily participation in operations is generally restricted. On the other hand, business police officers, including the chief executive officer, CFO, and others, are tasked with the day-to-day monitoring of the company, implementing the approaches accepted by the board to drive productivity and development. Their responsibilities consist of everything from financial administration to calculated planning and functional oversight. The interaction in between these duties makes certain that a company maintains an equilibrium of power and liability, critical for healthy governance and business success. The performance of a firm frequently pivots on just how well these teams communicate and fulfill their corresponding roles, adding to the general sustainability and development of the company.
Company Framework and Administration in Service Companies
In the complex globe of organization firms, understanding the ins and outs of company framework and governance is critical for both stakeholders and administration. The business framework of a company corporation is normally determined by its lawful type, which can vary from restricted obligation companies to publicly traded firms, each with its distinct set of responsibilities and policies. At the core of this framework is the board of supervisors, in charge of making essential strategic choices and overseeing the overall direction of the company. This board usually includes a mix of interior and exterior participants, each bringing a varied set of skills and viewpoints to the table. The exterior directors are particularly crucial in offering an unbiased view on management practices and firm plans, thus ensuring that the firm sticks to a high requirement of governance and liability. Furthermore, the role of the CEO, that commonly functions as the bridge between the corporation and the board's day-to-day operations, is essential. The chief executive officer should not just carry out the board's directives yet likewise preserve a dynamic strategy to taking care of the corporate staff and sources to accomplish calculated purposes. This dynamic is better complicated by the demand to balance shareholder interests with those of other stakeholders, consisting of employees, consumers, and the neighborhoods in which the firm operates. Efficient business administration therefore requires a well-defined, clear process, which is usually encapsulated in the firm's bylaws. These bylaws set forth the procedures for attending to different company affairs, including the consultation and removal of supervisors, the organizing and conduct of board meetings, and the civil liberties and responsibilities of investors. By doing this, company administration serves as an important structure for maintaining the stability and performance of business procedures, making sure that the firm can adapt to changes in the marketplace and regulative setting while still meeting its responsibilities to stakeholders.
Strategic Management in Business Firms
In the dynamic realm of organization, companies are continuously adjusting to maintain competition and make certain lasting success. Strategic management plays a pivotal role in this procedure, functioning as the backbone for decision-making and direction-setting at every degree of the organization. At its core, critical management includes the solution, execution, and assessment of cross-functional choices that enable a company to accomplish its objectives. The process starts with senior leaders defining a clear vision and objective, which then assist the advancement of even more concrete strategies and goals. corporation real life examples -down technique guarantees that all campaigns are straightened with the company's overarching ambitions. Better, critical monitoring is not a static process however a continuous loop of analysis and change. Ecological scanning, an important component, includes the extensive evaluation of interior and external elements that affect the firm. This includes reviewing market patterns, rival actions, technological advancements, and governing adjustments, along with internal efficiency metrics. Insights acquired from this analysis notify strategic choices, allowing organizations to profit from possibilities and alleviate possible threats. As an example, a technology company might move its emphasis in the direction of expert system and artificial intelligence based on patterns showing considerable development in these industries. Critical administration encompasses the appropriation of sources to ensure optimal execution of strategies. This calls for a fragile balance between long-lasting objectives and short-term goals, usually demanding compromises that are purposefully justified. Effective resource allowance additionally includes determining vital efficiency indicators (KPIs) that are used to determine development and identify the performance of applied methods. Adjustments are made based on these performance end results, bring about a refined strategic strategy. In general, the relevance of critical management in business companies can not be understated. It not only gives a roadmap for navigating the complicated business landscape yet likewise integrates numerous practical locations of the company, guaranteeing cohesiveness and harmony. Through mindful preparation, extensive analysis, and consistent adjustment, tactical management helps companies not simply to endure however to prosper in today's ever-evolving market settings.
